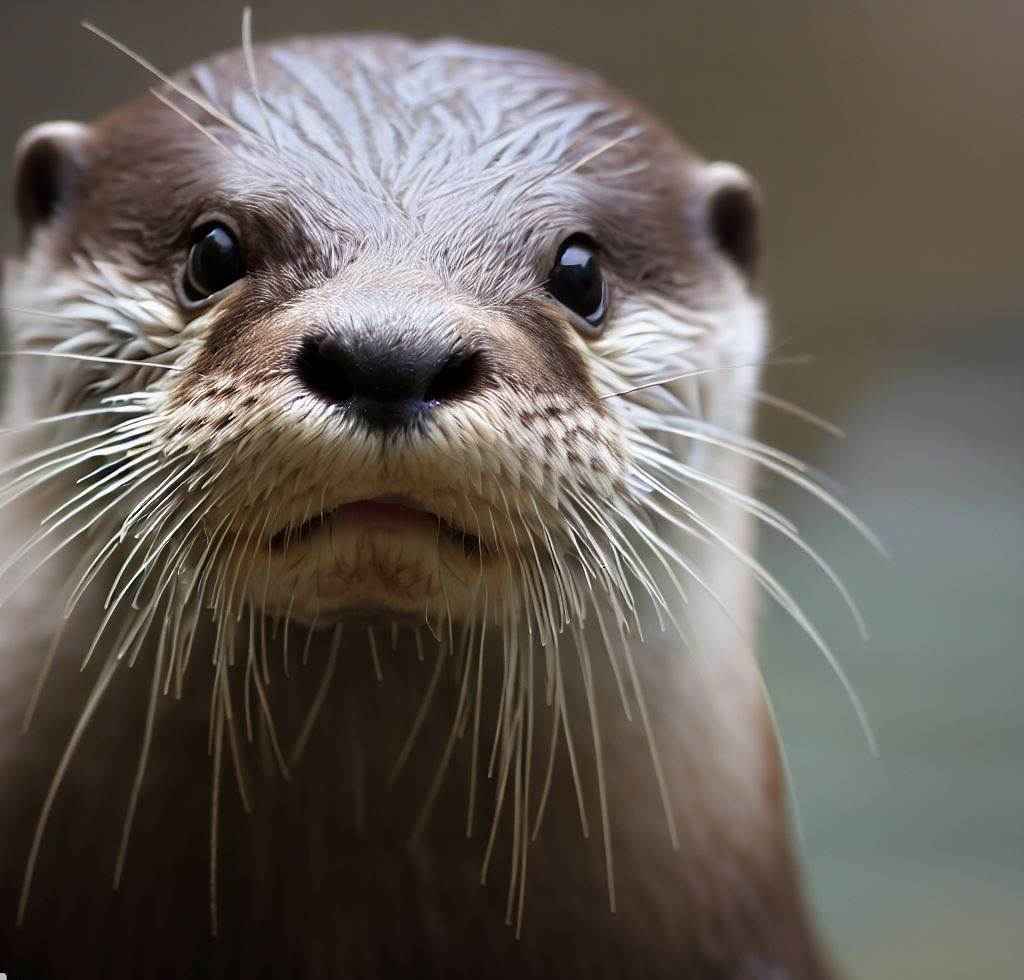
Why Do Otters Eat Ducks?
Answer to the question Do Otters Eat Ducks? Yes, Otters do eat ducks to fulfill their hunger. These are selective predators meaning that they eat anything which is available in their environment including ducks. However ducks are not the principal food source for otters. Instead, they are more likely to take advantage of them when other food supplies are low or when an easy chance arises. Otter species are mostly carnivorous, feeding on fish, crabs, and small aquatic animals. They mostly consume fish but there have been accounts of otters preying on ducks, particularly little ducklings.
They are active hunters, adapting their diet to the available food sources in their environment. Because ducks, particularly ducklings, are usually located near bodies of water, they can become prey for otters on occasion. However, such situations are actually unique, and otters do not represent a serious hazard to healthy adult ducks in general.
The otter will often consume fish, amphibians, and other aquatic invertebrates since these food sources are more numerous and accessible. Do otters eat ducks? Ducks, being nimble and alert birds, frequently avoid possible otter attacks. While otters occasionally hunt ducks but they also serve an important part in the ecosystem’s biodiversity.
Introduction:
But there is a common question among nature enthusiasts: Do otters eat ducks? Otters are fascinating creatures that inhabit various aquatic ecosystems around the world. They are known for their playful behavior and excellent swimming abilities. In this blog post, we will explore the dietary habits of otters and shed light on whether ducks are part of their menu.
Will Otters Eat Ducklings?
Fish, eels, frogs, eggs, birds, and small mammals like mice are all eaten by otters, who are predators. They have also been known to catch bigger animals, such as ducks.
Ducklings can be eaten by predatory predators like otters, who are renowned for their playful and adept hunting styles. This is especially true in places where otters and waterfowl cohabit. Ducklings are drawn to them because of their sharp fangs and quickness.
Building barriers or making sure the nesting and raising area is secure will help shield ducklings from otter predation. Recognizing the ecological interactions between otters and other species is essential to preserving the ecosystem’s equilibrium and protecting its most vulnerable inhabitants, such as ducklings.
Do Otters Eat Duckweed?
As carnivores, otters mostly consume fish, crabs and small animals. The little aquatic plant known as duckweed is incompatible with their diet. Otters are skilled underwater hunters who snatch prey with their keen teeth and fast claws.
Duckweed may be present in their environments but it does not significantly contribute to their diet. Their main concern is aquatic life which supplies the minerals needed for their carnivorous diet. Their gastronomic likes go more toward the fish and invertebrate smorgasbord.
Ways OF Otters To Hunt Ducks:
The hunting techniques employed by otters to target ducks are both fascinating and strategic. While otters primarily focus on a diet of fish, their opportunistic nature leads them to occasionally hunt ducks, particularly ducklings. Here are some unique ways otters go about hunting ducks:
1. Stealth and Ambush:
Otters are stealthy predators, silently gliding through the water to avoid detection. When targeting ducks, they use the element of surprise by hiding underwater or camouflaging among aquatic vegetation. They patiently wait for the perfect moment to strike, pouncing on unsuspecting prey with lightning speed.
2. Group Hunting:
Some otter species, like the African clawless otters, employ cooperative hunting techniques. They work together in small groups to create a strategic advantage. While one otter may distract the mother duck, others seize the opportunity to snatch ducklings from behind, taking advantage of the momentary confusion.
3. Underwater Pursuit:
Otters are agile swimmers, capable of navigating underwater with precision. When chasing ducks, they pursue them beneath the water’s surface, where ducks are less agile. Otters use their dexterity to outmaneuver their prey by relying on their keen senses to track the ducks’ movements.
4. Utilizing Riverbanks:
Otters are known to hunt ducks near riverbanks and shorelines, where ducks often congregate. They employ their sharp vision and awareness to spot potential prey from a distance. With a burst of speed, otters dive into the water, making quick dashes toward their target.
This is important to reiterate that otters mainly focus on fish and other aquatic creatures as their primary food source. Hunting ducks is not a regular part of their diet, and such instances are relatively uncommon. Otters play an essential role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitats, and their occasional interactions with ducks are a part of the complex web of life in the natural world. You can also know about what kinds of otters do otters eat?
Protection Of Ducks From Otters:
It is vital to protect ducks from possible predators such as otters in order to maintain the careful balance of aquatic environments. While otters may not pose serious danger to adult ducks, taking action to protect ducks and their fragile ducklings can help to improve their general well-being. Here are some strategies for protecting ducks from otters:
1. Habitat Management:
Creating and preserving diverse habitats along water bodies is essential for ducks to find suitable nesting and breeding grounds. Dense vegetation near the water’s edge can provide cover and protection for ducks and their offspring, reducing the risk of otter predation.
2. Predator Deterrents:
Implementing predator deterrents near duck nesting sites can help keep otters at bay. Installing motion-activated lights, scarecrows, or reflective materials can deter otters and other potential predators from approaching nesting areas.
3. Nesting Platforms:
Ducks are vulnerable when nesting on the ground, making them easy targets for otters. Providing nesting platforms in the water can offer ducks a safer alternative, as otters are less likely to reach them in open water.
4. Predator Exclusion Fencing:
Installing predator exclusion fencing around duck nesting sites can create a barrier, preventing otters from accessing these areas. Properly designed fencing can be effective in deterring otters while allowing ducks to move freely.
5. Education and Awareness:
By promoting awareness about the importance of protecting ducks and other wildlife can encourage responsible behavior around water bodies. Educating the public on the function of otters in the ecosystem and the possible impact of human actions on animals can help to promote a feeling of responsibility.
Humans can ensure the safety and well-being of ducks by enabling them to dwell in their natural habitats while maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems. Responsible conservation activities may promote harmonious relations among otters, ducks, and other species, therefore increasing the biodiversity of our natural environment.
Food That Otters Often Eats:
Otters have a diverse and adaptable diet that mainly revolves around aquatic prey. As carnivorous creatures, they primarily consume a variety of marine life to sustain their energetic lifestyles. Here are some foods that otters often eat:
1. Fish:
Fish constitute the most significant portion of an otter’s diet. They are skilled fish hunters, preying on species like salmon, trout, perch, and catfish. Otters’ streamlined bodies and powerful tails make them agile swimmers, allowing them to chase and catch fish with remarkable efficiency.
2. Crustaceans:
Crabs, crayfish, and other crustaceans are also favorite delicacies for otters. Using their dexterous paws, they adeptly manipulate shells to extract the succulent meat inside.
3. Amphibians:
Otters have a penchant for amphibians, such as frogs and newts. They actively forage along the water’s edge and in marshy areas to find these protein-rich morsels.
4. Mollusks:
Mussels, clams, and snails are included in an otter’s diet, which they find in rivers and estuaries. To access the mollusks’ soft flesh, otters utilize their strong teeth to crack open the shells.
5. Birds:
Though not a primary food source, otters occasionally target birds, particularly ducklings, when the opportunity arises.
Otters are amazing feeders by adjusting their diet based on the seasonal availability of prey in their habitat. Their well-rounded diets and vital roles as predators contribute significantly to the health and balance of aquatic ecosystems. Conservation efforts aimed at preserving these ecosystems benefit not only otters but also the entire array of species that depend on these precious waterways. another question about otters is Do otters lay eggs? visit the post if you want to know about it.
What Type Of Feeders Are Otters?
Otters are classified as carnivorous feeders, indicating that their diet primarily consists of animal-based foods. As skilled hunters and swimmers, otters are perfectly adapted to their semi-aquatic lifestyles, making water their natural hunting ground. Their diet predominantly comprises a wide range of aquatic prey. Fish form a significant portion of their meals, and otters display impressive fishing skills.
With streamlined bodies and webbed feet, they glide effortlessly through the water, chasing and catching various fish species like salmon, trout, and catfish. Otters enjoy crustaceans such as crabs and crayfish, which they collect along riverbanks and in shallow waterways, in addition to fish. They have also been observed eating amphibians such as frogs and newts. Mollusks, such as mussels and clams, are also part of their diet, and otters use their powerful teeth to tear apart shells and get the delicious flesh within.
Whereas otters are generally carnivorous, they do display some opportunistic behavior, preying on tiny birds such as ducklings when the opportunity comes. Nonetheless, birds do not comprise a significant component of their daily food. Otters are as apex predators in their watery environments. They play an important role in preserving ecological balance by limiting prey numbers. Their food habits highlight the need of maintaining aquatic environments, which not only house otters but also a varied range of species that contribute to the health and richness of our planet’s biodiversity.
Facts & Features Of Otters:
Otters are fascinating creatures with a plethora of intriguing facts and unique features that set them apart in the animal kingdom. Here are some facts & features of otters:
- They are partially aquatic animals, meaning they can live on land as well as in water.
- Otters exhibit playful behavior when engaging in activities like sliding down muddy banks, playing with objects, and chasing each other.
- Otters are superb swimmers, because of their thick fur, which offers good insulation and buoyancy in the water.
- Their streamlined bodies and webbed feet allow them to maneuver with ease, making them highly efficient hunters.
- Otters have two layers of fur – a dense undercoat and longer guard hairs on top. The fur traps air, providing insulation and keeping them warm in chilly waters.
- Otters groom their fur regularly to maintain its waterproofing qualities.
- Numerous otter species are threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and illegal hunting.
- Conservation efforts are required to safeguard these endearing creatures and their critical roles in the maintenance of healthy aquatic environments.
FAQs:
1 What animal do otters eat?
Otters primarily eat fish, but they also consume crustaceans, amphibians, and mollusks as part of their diet.
2 Can otters eat chicken?
Otters are primarily carnivorous and typically do not eat chicken. Their diet mainly consists of fish, crustaceans, amphibians, and other aquatic prey found in their natural habitats.
3 Do otters eat goldfish?
Yes, otters are known to eat goldfish when they are available in their environment. Goldfish can be an easy target for otters due to their slow movements and presence in various water bodies.
4 What mammals do otters eat?
Otters primarily eat fish, but they also consume other aquatic prey, including crustaceans, amphibians, and mollusks. While they occasionally target small mammals, such as rodents, their diet mainly revolves around marine life.
5 What is an otters favorite animal?
An otter’s favorite animal is not a distinct species, as they primarily prefer fish, crustaceans, and other aquatic prey found in their habitat. Their diet revolves around various aquatic creatures rather than a specific favorite animal.