Do Beavers Eat Wood? Eating Secret Of Beavers:
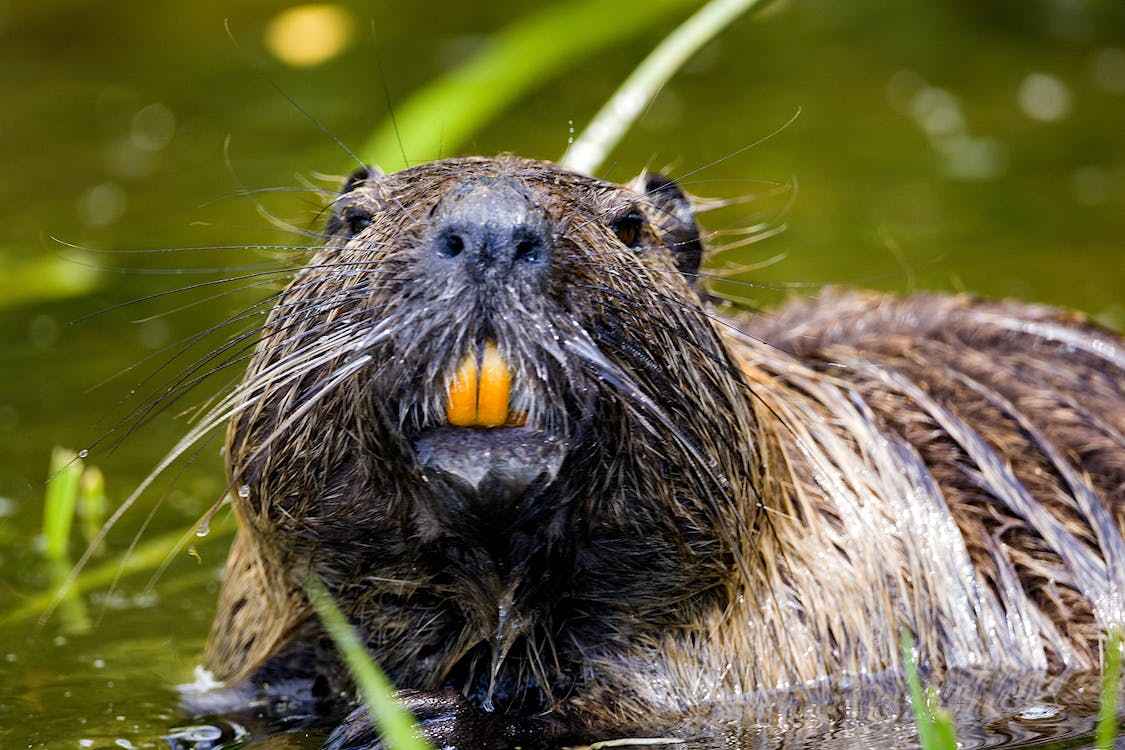
Answer to question Do Beavers Eat Wood? Yes, beavers eat soft layers of wood like tree bark. The fact is that wood is a fundamental part of beavers’ diet. They are herbivorous animals and their food comes from a variety of vegetation found near water bodies is a primary source of food. Their diet mainly consists of the following:
Tree Bark:
Beavers have strong, chisel-like incisor teeth that grow continuously throughout their lives. They use these teeth to gnaw through the bark of trees. Barks Of tree provides essential nutrients and also serves as their main food source during winter when other vegetation may not be as readily available.
Woody Stems:
Apart from tree bark, beavers also consume woody stems and twigs of various trees and shrubs. They are capable of felling small trees to access the branches and stems they prefer to eat.
Aquatic Plants:
Although wood makes up a significant portion of their diet, beavers also consume aquatic plants such as water lilies, pondweed, and cattails. These plants provide additional nutrients and variety to their diet.
Reasons for Eating Wood:
You might wonder why beavers predominantly consume wood when they have access to other vegetation. There are several reasons behind this behavior:
Nutritional Requirements:
They are large rodent species that require a sufficient amount of energy to maintain themselves. The inner bark wood which is rich in nutrients and provides them with the calories they need to stay active and healthy.
Dental Health:
As mentioned earlier beavers’ teeth grow continuously and they need to gnaw on hard substances like wood to wear down their teeth and prevent them from becoming too long. This constant gnawing also helps maintain their dental health.
Creating Habitat:
Beavers are well-known for their dam-building abilities. They use wood to construct dams across streams and rivers, creating ponds that serve as their habitats. By consuming wood they can play a vital role in shaping the ecosystem and creating environments suitable for various other wildlife.
Food Storage:
Beavers also store logs and branches underwater near their lodges to provide a readily available food supply during harsh winters when venturing outside becomes challenging.
By utilizing wood in these various ways, beavers prove to be crucial components of their ecosystems by promoting biodiversity and influencing the surrounding landscape.
Introduction:
One question that often comes to mind is Do beavers eat wood? Beavers with their distinctive flat tails and impressive dams and are fascinating creatures that play a crucial role in the ecosystem. In this context, we will delve into the dietary habits of these industrious rodents and shed light on their unique eating habits.
Why Do Beavers Eat Wood?
Beavers consume wood as their primary diet due to a combination of evolutionary adaptation and nutritional necessity. Their digestive system is equipped to break down cellulose, the main component of wood with the help of symbiotic bacteria. This process extracts the nutrients trapped within the wood’s fibrous structure that allows beavers to access otherwise unavailable energy sources.
Wood-eating also serves other crucial purposes for beavers. Gnawing on trees helps control their ever-growing teeth which continuously grow throughout their lives. Chewing wood also aids in maintaining their territory, constructing dams and building lodges for shelter. These lodges provide protection from predators and harsh weather as well as a safe environment to raise their young.
Ultimately, the beaver’s wood-based diet is a result of their unique ecological niche as ecosystem engineers. By transforming their surroundings through dam construction and tree felling, beavers create wetland habitats that benefit various species. This behavior showcases the intricate balance between an animal’s biology, its environment and its role in shaping ecosystems.
Are Beavers Semi-Aquatic Animals?
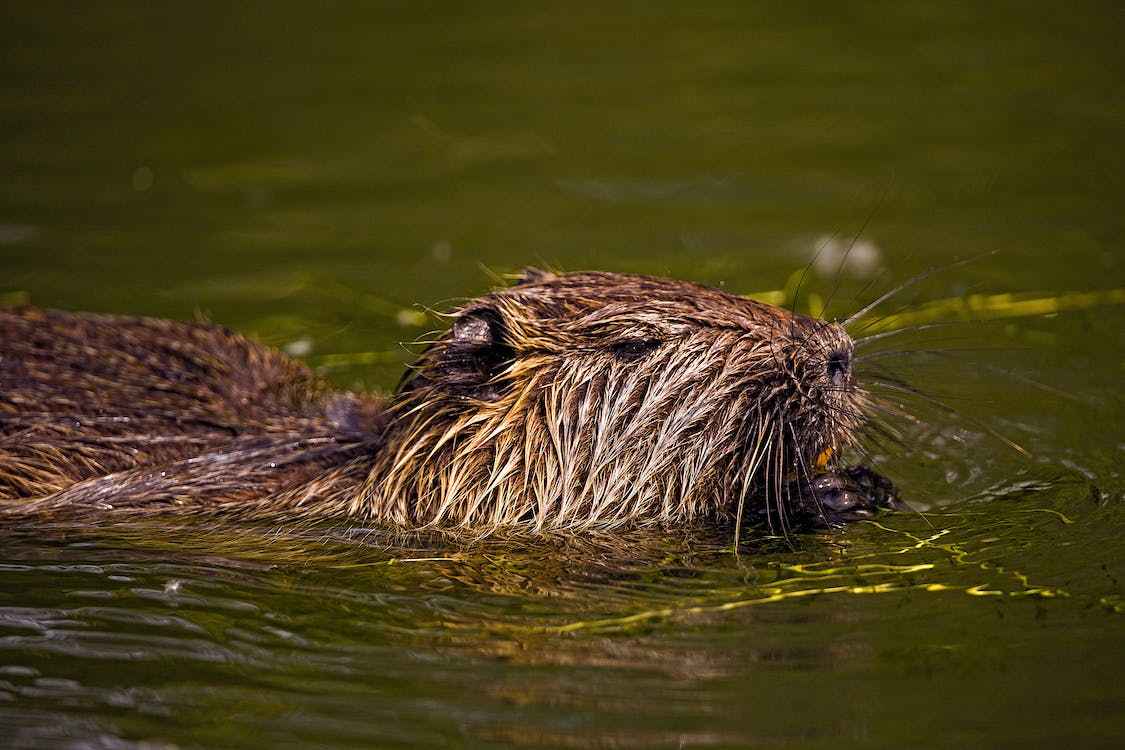
Beavers are fascinating semi-aquatic creatures, displaying remarkable adaptations for both land and water environments. As members of the rodent family, they have earned renown for their exceptional skill in constructing dams and lodges within freshwater ecosystems. In their semi-aquatic lifestyle, beavers spend a considerable amount of time in the water, where they construct their iconic dams using sticks, mud, and stones.
These dams serve multiple purposes, including creating deep ponds that provide protection against predators and storing food for the winter months. The ponds also serve as access points to their lodges, which are their sheltered homes built within the dam. While beavers are superb swimmers, they are not limited to aquatic activities alone. They venture onto land to forage for food and to fell trees, which they use as a vital food source. Beavers possess webbed hind feet, aiding them in swimming efficiently, and sharp claws and strong teeth, enabling them to cut through wood with ease.
Their ability to thrive in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats makes beavers a remarkable example of adaptation and resourcefulness in the animal kingdom. By embracing a semi-aquatic lifestyle, they play an essential role in shaping their ecosystems and providing a home for numerous other species, demonstrating their importance as ecological engineers.
Importance Of Beavers To the Environment:
The importance of beavers to the environment cannot be overstated. One of the primary contributions of beavers lies in their dam-building activities. By constructing dams across streams and rivers, they create expansive ponds that serve as essential habitats for various aquatic creatures. These ponds also help to regulate water flow, preventing flooding during heavy rains and ensuring a steady water supply during dry periods.
Furthermore, beaver dams contribute to improving water quality. The ponds created by these industrious animals act as natural filters, trapping sediment and pollutants, leading to clearer and cleaner water downstream. This, in turn, promotes a healthier environment for fish and other aquatic organisms. Beavers also play a significant role in increasing biodiversity. Their preference for certain tree species leads to the creation of diverse habitats, attracting a wide array of wildlife. These newly established wetland areas become havens for amphibians, birds, and insects, enriching the ecosystem’s overall biodiversity.
Additionally, Why do beavers eat wood? Beavers’ foraging habits, particularly their consumption of wood and vegetation, help to control plant overgrowth, ensuring a healthy balance within the ecosystem. This selective grazing stimulates new growth, fostering a more diverse plant community. In essence, beavers act as ecosystem engineers, sculpting landscapes and fostering biodiversity. Their remarkable ability to modify their environment positively influences water flow, water quality, and species diversity. Recognizing the importance of beavers in maintaining healthy ecosystems is essential for our understanding of nature’s delicate balance and the need to conserve these extraordinary creatures for the benefit of our planet.
Habitat & Food Of Beavers:
Beavers are commonly found in regions across North America, and Europe. The construction of dams is a defining feature of beavers’ habitat. These dams serve multiple purposes, such as creating deep ponds that provide protection against predators and ample water access for the beavers. The lodges, built within the dams, offer shelter and safety from predators and harsh weather conditions.
The strategic location of their habitats not only benefits the beavers but also plays a vital role in shaping the surrounding ecosystem. In terms of food, beavers are herbivorous creatures with a predominantly vegetarian diet. Their diet primarily consists of tree bark, especially the inner bark, which is rich in nutrients and a valuable energy source. Beavers are proficient tree fellers, using their sharp incisor teeth to gnaw through the bark and access the nutritious inner layers.
Apart from tree bark, beavers also consume woody stems, twigs, and aquatic plants. During warmer months, they forage for various vegetation, while in winter, when their food options are limited, they rely heavily on the stored logs and branches from their food caches. Overall, beavers’ habitat and food preferences are intricately linked, influencing their lifestyle as ecological engineers and highlighting their essential role in shaping and maintaining the ecosystems they inhabit. Another question is How strong are raccoons? If you want to know about them visit my other post.
How Beavers Cut Trees And Build Dams?
Beavers are nature’s engineers, and their ability to cut trees and build dams is truly remarkable. These semi-aquatic creatures employ a combination of physical adaptations and instinctual behavior to accomplish these impressive feats. When beavers set out to cut trees, they utilize their most iconic tools – their incisor teeth. These teeth are incredibly strong and continuously grow throughout their lives. To ensure their teeth stay at an optimal length, beavers constantly gnaw on wood.
Their unique enamel composition allows the front surfaces of their teeth to wear away more slowly than the softer back surfaces, creating sharp, chisel-like edges that are perfect for cutting through tough bark and wood. Once they’ve successfully felled a tree, the beavers then use their powerful front legs and claws to drag the logs to the desired location for dam construction. Alongside their teeth and limbs, their broad, flat tails also play a crucial role. Beavers use their tails as a tool for patting down mud and vegetation while building their dams, helping to create stable structures.
The dam-building process is a cooperative effort among beaver family members. They gather sticks, branches, mud, and stones, meticulously arranging them to create a sturdy barrier. The dams are not only essential for creating ponds that serve as their homes and protection against predators but also help to regulate water flow and maintain water levels during dry periods. Beavers’ exceptional skills in tree cutting and dam building not only demonstrate their resourcefulness but also highlight their significant impact on their ecosystems. Through their engineering prowess, they transform landscapes, creating diverse habitats for various plant and animal species and exemplifying the harmonious relationship between animals and their environment.
Facts & Features Of Beavers:
Beavers, the industrious semi-aquatic rodents, boasts an array of fascinating facts and unique features that make them truly captivating creatures. Here are some key insights into these remarkable animals:
- Beavers are well-adapted to their aquatic lifestyle.
- Beavers are renowned for their dam-building prowess.
- They construct dams across streams using sticks, mud, and stones.
- These dams create ponds that serve as sheltered habitats, food storage, and protection from predators. Beavers possess strong, self-sharpening incisor teeth that never stop growing.
- This behavior helps them avoid potential predators and work on their engineering projects with reduced risks. Beavers typically live in family units called colonies.
- A colony consists of a monogamous pair (adult male and female), their offspring, and sometimes young beavers from previous years.
- Their dam-building activities significantly alter landscapes, creating wetland habitats that benefit numerous other species and enhance biodiversity.
- Beavers communicate with a range of vocalizations, body postures, and tail slapping on the water’s surface to warn others of potential dangers.
- While beaver populations are relatively stable, they were once overhunted for their valuable fur.
- Conservation efforts have helped protect and restore their habitats in many regions.
- These remarkable facts and features of beavers exemplify their vital role as ecosystem engineers and their significant contributions to maintaining the delicate balance of nature.
- Their intelligence, resourcefulness, and adaptability make them truly iconic animals in the natural world.
FAQS:
1 What does a beaver eat?
Beavers primarily eat tree bark, woody stems, and aquatic plants. Their diet consists of a variety of vegetation found near water bodies.
2 How much wood can a beaver eat?
A beaver can eat approximately 2 to 4 pounds (0.9 to 1.8 kilograms) of wood per day, depending on factors like age and availability of other food sources. Their impressive wood consumption is essential for their nutritional needs and dental health.
3 How do beavers find wood?
A beaver can eat approximately 2 to 4 pounds (0.9 to 1.8 kilograms) of wood per day, depending on factors like age and availability of other food sources. Their impressive wood consumption is essential for their nutritional needs and dental health.
4 Why does beaver chew wood?
Beavers chew wood primarily for two reasons: to obtain essential nutrients from the inner bark, which forms a significant part of their diet, and to wear down their constantly growing incisor teeth, preventing them from becoming too long and ensuring dental health.
5 Why do beavers build dams?
Beavers build dams to create ponds that serve as sheltered habitats, provide protection from predators, and store food for the winter months. Additionally, these dams help regulate water flow, ensuring a steady water supply during dry periods and contributing to the overall health of their ecosystem.
6 Do beavers eat wood or just chew it?
Beavers both eat and chew wood. They consume it as their main food source for extracting nutrients using special bacteria. Chewing also helps regulate their teeth growth and aids in construction for dam-building and shelter.